What Are Metalized Polypropylene Films and Their Core Characteristics?

Metalized polypropylene films are thin layers of polypropylene coated with a metal, usually aluminum or zinc. This coating is applied by vapor deposition, creating a shiny, reflective surface. The base material is polypropylene, a type of plastic known for its clarity, strength, and chemical resistance. When metalized, this film gains enhanced barrier and electrical properties, making it useful for many industrial applications.
What is Metalized Polypropylene Film? Definition and Material Composition
Metalized polypropylene film, often called metallized BOPP (biaxially oriented polypropylene), starts as a clear plastic film. This film is stretched in two directions to improve strength, clarity, and flexibility. Then, a thin metal layer is added in a vacuum chamber.
- Base layer: Polypropylene film, thin and clear.
- Metal coating: Aluminum or zinc, very thin (nanometer scale).
- Thickness: Typically ranges from 12 to 100 microns for the plastic, with the metal layer being less than 0.1 microns.
This construction blends the flexibility and chemical resistance of polypropylene with the reflective and barrier features of the metal layer.
Key Physical and Chemical Properties
Metalized polypropylene films have several important physical and chemical properties that directly affect their performance.
| Property | Description | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Total film thickness including metal coating | 12 – 100 microns (plastic layer) |
| Gloss | Shiny surface thanks to metal layer | High gloss, 80-95% reflectance |
| Surface Energy | Indicates how well adhesives and inks stick | 35-45 dynes/cm (improved by metal) |
| Tensile Strength | Force the film can bear before breaking | 50–150 MPa |
| Elongation | Stretch before breaking (%) | 100-250% |
| Tear Resistance | Resistance to tear initiation and growth | Moderate to high |
These metrics make the film strong, flexible, and able to bond well with adhesives or inks.
How Does Metallization Enhance Polypropylene Films?
Adding a metal layer changes polypropylene films in many ways:
- Barrier properties: The metal acts as a shield against light, oxygen, moisture, and gases.
- Electrical conductivity: Metalized films can conduct electricity, important for capacitor use.
- Thermal reflectivity: Reflects heat and light, which helps in insulation.
- Aesthetic improvement: Shiny, metallic finish used in packaging and decoration.
- Mechanical strength: Slightly improved tear resistance and stiffness due to metal layer.
The common metals used, aluminum and zinc, each offer different qualities. Aluminum gives a high gloss and excellent barrier. Zinc is sometimes preferred for specific capacitor designs due to its electrical properties.
Differences Between Metalized Polypropylene and Other Plastic Films
To understand metalized polypropylene films, it helps to compare them with other popular plastic films.
| Film Type | Key Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| PET | Very stiff, high temperature resistance, chemical resistant, excellent clarity | Durable packaging, outdoor labels |
| PVC (Vinyl) | Flexible, good UV resistance, soft in heat | Outdoor graphics, billboards |
| PE (Polyethylene) | Soft, good chemical resistance, flexible | Food packaging inner layers |
| Metalized PP | Flexible, glossy, strong barrier against moisture and gases, metal reflective | Capacitors, food packaging, insulation films |
Metalized polypropylene stands out for its balance of flexibility, gloss, and barrier properties, alongside metal’s electrical and reflective benefits.
Typical Manufacturing Processes
Making metalized polypropylene films involves several steps:
- Drying: Polypropylene resin pellets are dried to remove moisture.
- Extrusion: Pellets are melted and extruded into a thin film.
- Biaxial stretching: The film is stretched in two directions to improve strength and clarity.
- Corona treatment (optional): Surface is treated to raise energy for better metal adhesion.
- Metal vapor deposition: Aluminum or zinc is vaporized in a vacuum chamber and deposited evenly on one side of the film.
- Winding and inspection: The metalized film is wound onto rolls and quality checked for thickness, uniformity, and defects.
This controlled process ensures consistent film quality and performance.
Critical Parameters Influencing Film Performance in Applications
Several factors matter when choosing or using metalized polypropylene films:
- Dimensional stability: The film must maintain shape without shrinking or deforming, especially when heated.
- Clarity and gloss: Important for packaging and decorative uses.
- Conformability: The film should smoothly adhere to curved or irregular surfaces.
- Surface energy: High enough to bond with inks and adhesives.
- Thickness uniformity: Ensures consistent barrier and electrical properties.
If these parameters are off, the film may fail in its application, causing leaks, poor print quality, or electrical faults.
Environmental and Durability Considerations
In industrial or consumer use, the film faces diverse conditions.
- Moisture resistance: The metal layer blocks moisture vapor effectively.
- UV stability: Polypropylene resists UV damage better than many plastics, but prolonged exposure can cause yellowing. Often UV stabilizers are added.
- Chemical resistance: Polypropylene resists many acids, bases, and solvents, ensuring durability around chemicals.
- Temperature tolerance: Typically stable from -40°C to 90°C continuously; short peaks above 100°C possible.
With these properties, metalized polypropylene film can endure in packaging, electronics, and industrial settings.
By examining these key points, you see why metalized polypropylene films are vital in today’s advanced materials. Their unique blend of strong polypropylene film properties plus metallized features gives them versatility and strength—perfect for many industries.
What Are the Major Applications for Metalized Polypropylene Films?

Metalized polypropylene films have become key components across many industries. Their unique blend of physical strength, electrical performance, and visual appeal makes them highly versatile. Let’s examine various applications for metalized polypropylene films by diving into their important roles in packaging, electrical components, electronics, renewable energy, decorative finishes, and industrial uses.
How is metalized polypropylene film used in packaging?
Metalized polypropylene (PP) film is valued in packaging for barrier properties, printability, and food-grade safety.
- Barrier Properties: When coated with a thin metal layer, usually aluminum, the film blocks moisture, oxygen, and light effectively. This barrier keeps food fresh, prevents spoilage, and extends shelf life. It acts as a low-cost alternative to laminated film structures.
- Printability: The smooth metalized surface provides excellent gloss and allows sharp, vibrant printing. This quality benefits labels and packaging that need high visual impact.
- Food Safety: Metalized PP is generally food-contact approved. It resists common food ingredients like oils and acids without degrading or transferring flavors.
This makes metalized polypropylene films a popular choice for snack wraps, snack bags, candy packaging, and coffee pouches. Their lightweight nature facilitates cost-effective shipping and handling while supporting consumer safety.
Role of metalized polypropylene films in electrical capacitors
One of the most important industrial applications of metalized polypropylene films is in capacitor manufacturing, especially metallized polypropylene film capacitors.
- Dielectric Properties: Polypropylene film acts as a dielectric. Its resistivity and low dielectric losses make it ideal for storing and releasing energy with minimal heat buildup.
- Self-Healing Ability: These films are metal-coated with aluminum or zinc, then rolled into compact cylinders in capacitors. If a small fault happens, the thin metal layer quickly vaporizes at the fault site, isolating the defect and restoring insulation. This greatly extends capacitor life.
- High Voltage Handling: Metalized polypropylene capacitors can handle voltages typically up to 1000 volts or more. This high voltage tolerance suits them for power electronics and high-frequency circuits.
In practice, these capacitors improve power supplies by smoothing voltage spikes, enhance audio equipment with noise filtration, and optimize lighting circuits through power factor correction. Their long lifespan and reliability are critical in industrial and consumer electronics.
Applications in electronics beyond capacitors
Metalized polypropylene films also serve key functions beyond capacitors in electronics:
- Signal Filtering: The film’s stable dielectric properties support precision electronic filters that reduce unwanted noise.
- Electrical Insulation: Thin, metalized PP films act as insulation layers in circuit boards and components to prevent shorts.
- Noise Reduction: Using metalized films, engineers reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI) in sensitive electronics.
This makes metalized polypropylene suitable for telecommunications, automotive electronics, and audio equipment where signal integrity is vital.
Use in renewable energy systems
Metalized polypropylene films are essential for emerging renewable energy applications.
- Capacitors for Power Quality: Renewable energy systems like solar and wind require stable power delivery. Metalized polypropylene capacitors smooth voltage fluctuations and filter harmonics.
- Energy Storage Improvements: These capacitors contribute to higher energy storage efficiency in inverters, converters, and electric vehicle (EV) battery management systems.
Their stability at various temperatures and long operational life help renewable energy devices become more reliable and efficient.
Decorative and printing applications
Metalized polypropylene films also feature in decorative uses where shine and print quality matter:
- Labels and Overlays: Their smooth, reflective surface highlights graphics with vibrant colors and sharp details.
- Aesthetic Finishes: They provide metallic gloss and bright finishes that appeal in consumer goods packaging, promotional stickers, and product wraps.
Because these films balance durability and visual appeal, they suit wide-ranging indoor uses with cost advantages over more expensive metal foils.
Industrial uses such as insulation films, protective covers, and moisture barriers
Industries use metalized polypropylene films for practical protective functions:
- Insulation Films: Their dielectric and heat resistance properties make them useful for electrical insulation layers.
- Protective Covers: Metalized PP films shield machinery and surfaces from dust, moisture, and abrasion.
- Moisture Barriers: The metal coating forms an effective vapor barrier for industrial packaging and storage covers.
This durability combined with light weight supports applications in automotive, aerospace, and construction sectors.
Comparative application strengths versus other metalized films or alternatives
Metalized polypropylene films compete mainly against metalized PET, PVC, and PE films.
| Film Type | Barrier Quality | Printability | Electrical Use | Durability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metalized PP | Very good moisture & gas barrier | High gloss, excellent printing | Excellent dielectric, self-healing capacitors | Good mechanical, chemical resistance | Moderate (economical) |
| Metalized PET | High dimensional stability, chemical & thermal resistance | Very high print quality | Less self-healing capability | High strength, good UV resistance | Higher than PP |
| Metalized PVC | Good barrier but less chemical resistance | Flexible, good printability | Limited electrical use | Flexible but brittle in cold | Moderate |
| Metalized PE | Moderate barrier but good moisture resistance | Lower gloss, limited printability | Limited electrical | Flexible, less strong | Low (economical) |
Metalized polypropylene films offer a balanced mix of low cost, dielectric performance, and barrier function, making them highly favored especially in packaging and electrical capacitor roles.
What industries commonly use metalized polypropylene films?
Across industries, metalized polypropylene films serve critical roles:
- Packaging: Food, beverage, pharmaceuticals, and personal care.
- Electronics: Capacitors in audio devices, power supplies, telecommunications, automotive and aerospace circuits.
- Renewable Energy: Solar and wind inverters, EV power management.
- Industrial: Insulation, protective films, moisture barriers.
- Printing and Decoration: Product labels, promotional wraps, and decorative applications.
How do metalized polypropylene films benefit electrical components like capacitors?
In capacitors, metalized polypropylene films boost performance through:
- High Capacitance: The high dielectric constant allows more charge storage in smaller volume.
- Self-Healing: Improves reliability by isolating faults automatically.
- Low Dielectric Loss: Saves energy and improves efficiency.
- High Voltage Tolerance: Suits high stress environments.
- Long Lifespan: Reduces maintenance costs and downtime.
Their combination of electrical stability, durability, and compactness make them vital in modern high-tech electronics and renewable energy applications.
What Are the Performance Benefits and Selection Criteria for Metalized Polypropylene Films in Various Applications?
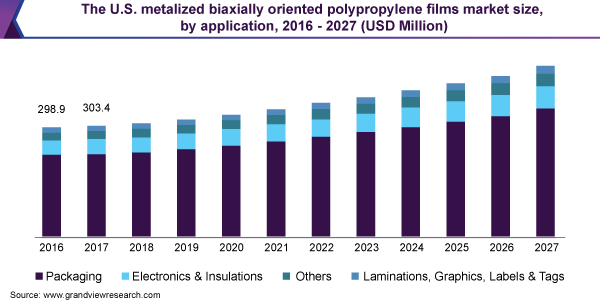
When you examine various applications for metalized polypropylene films, understanding their performance benefits and choosing the right film is key. These films play a critical role in many electrical and industrial uses, especially in capacitors and power electronics. Let’s look at why these films stand out and how to pick the best one for your needs.
Key Advantages of Metalized Polypropylene Films in High-Frequency Circuits and Power Electronics
Metalized polypropylene films excel in high-frequency circuits and power electronics for several reasons:
-
High Capacitance and Energy Storage: The films have a high dielectric constant, allowing capacitors to store more electrical energy efficiently. This is vital when you need power to flow smoothly in devices such as power supplies or motor controls.
-
Low Dielectric Loss: These films lose very little energy as heat. This low loss means devices using them can run cooler and more efficiently, improving performance and safety.
-
High Voltage Resistance: Metalized polypropylene films withstand high voltages without breaking down. This feature is crucial for circuits handling strong electrical loads, such as renewable energy converters.
-
Stable Electrical Properties: They maintain consistent performance even under varying temperatures and frequencies, important in audio equipment and avionics where signal clarity is crucial.
-
Lightweight and Compact: Compared to other capacitor materials like aluminum electrolytics, these films enable lighter, more compact designs that save space without sacrificing performance.
How Self-Healing Property Enhances Capacitor Lifespan
One remarkable benefit is the self-healing property of metalized polypropylene films. Here’s how it works:
-
When a tiny defect or short circuit appears in the film, a small area around it vaporizes the metal coating.
-
This "burns away" the fault, isolating the damaged zone so the rest of the capacitor keeps working.
-
This built-in repair mechanism prevents total capacitor failure, dramatically extending its lifespan.
This feature is a reason these capacitors are trusted in critical systems like aerospace electronics and power grids, where failure is not an option.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Metalized Polypropylene Films
Choosing the right metalized polypropylene film depends on your specific application. Here are the key criteria you should evaluate:
| Selection Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Capacitance | Match the capacitance value with your circuit’s needs to ensure proper energy storage and filtering. |
| Voltage Rating | Confirm the film can handle maximum voltage levels for safety and durability. |
| Temperature Range | Check thermal limits; some films perform well up to 105°C or higher, ideal for harsh environments. |
| Mechanical Durability | Assess tensile strength and tear resistance to withstand physical stress during winding and operation. |
Evaluating these factors helps prevent premature failure and optimizes device performance.
Impact of Film Properties on Application Outcomes
The physical properties of the metalized polypropylene film influence how it performs in different environments. Consider the below features:
-
Gloss and Clarity: High gloss improves optical appeal and print quality for decorative applications, while clarity matters for labels and overlays.
-
Surface Energy: This affects how well ink adheres for printing or how adhesives bond, critical for packaging uses.
-
Shrinkage: Films with low shrinkage maintain dimensional stability in heat-sensitive applications, preventing distortion or electrical failures.
Other useful mechanical properties include:
-
Tensile Strength: The force required to stretch the film affects handling during manufacturing and durability in use.
-
Elongation and Tear Resistance: These impact film flexibility and resistance to tearing during assembly and operation.
Ensuring the right combination of these factors avoids defects and maintains performance integrity.
Maintenance and Handling Best Practices
Preserving the film's and capacitor’s integrity requires proper maintenance and handling:
-
Use Correct Polarity: Capacitors must be connected properly to avoid reverse voltage damage.
-
Store in a Cool, Dry Place: Avoid heat and humidity that can degrade the film.
-
Avoid Direct Sunlight and Mechanical Stress: Prolonged exposure can cause film brittleness or warping.
-
Routine Inspection: Check capacitors for signs of damage or aging, and replace if necessary to prevent faults in critical circuits.
Following these guidelines extends service life and reduces risks of failure.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
The metalized polypropylene film industry is evolving with new advancements:
-
Improved Metallization Techniques: Finer metal layers enhance capacitance and self-healing effectiveness.
-
Nanotechnology: Development of nanoparticle coatings boosts barrier and thermal properties.
-
Hybrid Films: Combining polypropylene with other polymers improves temperature tolerance and mechanical strength.
-
Environmentally Friendly Materials: Focus on recyclable and low-emission films aligns with green technology goals.
Such innovations expand application potential, especially in renewable energy and electric vehicles.
Cost-Performance Balance and Economic Considerations
While metalized polypropylene films cost more up front than some alternatives, their performance justifies the investment:
-
Longer Lifespan: Reduces replacement and maintenance costs.
-
High Reliability: Minimizes downtime in critical systems, saving further expenses.
-
Energy Efficiency: Lower losses mean energy savings over time.
When selecting films, weigh the total cost of ownership instead of just initial pricing. In demanding industries like aerospace or automotive electronics, the premium pays off with superior safety and performance.
Why Choose Metalized Polypropylene Films for Critical Electrical Applications?
Because of their:
-
Exceptional electrical stability and low loss
-
Strong self-healing properties that prevent failure
-
High voltage capacity and wide temperature range
-
Mechanical strength and dimensional stability
These traits make them the top choice for power supplies, audio devices, motor drives, renewable energy systems, and advanced communication equipment.
What Factors Influence the Selection of Metalized Polypropylene Films for Different Industries?
Each industry prioritizes different factors:
| Industry | Primary Selection Factors |
|---|---|
| Automotive | High temperature resistance, vibration durability, compact size |
| Renewable Energy | High voltage rating, low losses, long lifespan |
| Consumer Electronics | Cost-effectiveness, gloss for aesthetics, dimensional stability |
| Aerospace | Extreme reliability, self-healing, mechanical strength |
| Packaging | Surface energy for printability, barrier properties, flexibility |
Understanding these needs helps you select the right film that fits your performance and cost goals perfectly.
Additional Table: Mechanical and Electrical Properties Overview
| Property | Importance in Application | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Durability during handling & use | 50–150 MPa |
| Elongation | Flexibility to prevent cracking | 100-250% |
| Tear Resistance | Resistance to damage during use | Moderate to high |
| Dielectric Loss | Energy efficiency in capacitors | Very low |
| Voltage Resistance | Safety and reliability in circuits | Up to 1000 V or more |
Conclusion
Thus, metalized polypropylene films combine excellent mechanical, optical, and electrical properties, making them essential in various applications from packaging to advanced electrical components. By understanding their performance benefits and selection criteria through the tables and details above, users can optimize application outcomes and maximize durability and cost-effectiveness.

FAQs about Examine various applications for metalized polypropylene films
What are the major applications for metalized polypropylene films?
The major applications for metalized polypropylene films include packaging (where their barrier properties and printability preserve food freshness), electrical capacitors (offering dielectric stability and self-healing), advanced electronics (for insulation and noise reduction), renewable energy systems (enhancing power quality and energy storage), decorative finishes (providing metallic gloss and sharp printing), and various industrial uses such as insulation and moisture barriers.
How is metalized polypropylene film used in packaging?
Metalized polypropylene film is used in packaging to provide a moisture, oxygen, and light barrier that extends product shelf life, while its smooth metal surface enhances printability for vibrant, sharp graphics; it is also food-safe and resists interaction with oils and acids, making it ideal for snack wraps, candy bags, and coffee pouches.
What role do metalized polypropylene films play in electrical capacitors?
Metalized polypropylene films function as dielectrics with low energy loss and high voltage tolerance in capacitors, and their unique self-healing property isolates faults by vaporizing the thin metal layer at defect sites, which extends capacitor lifespan and reliability in power electronics, audio, and lighting circuits.
What are the key benefits of metalized polypropylene films in high-frequency and power electronic applications?
Key benefits include high capacitance for efficient energy storage, extremely low dielectric loss for cooler operation, high voltage resistance to withstand strong electrical
Metalized polypropylene films combine strong materials with a thin metal layer for superior use. They offer great strength, durability, and electrical properties, making them top choices in packaging, electronics, and energy fields. Knowing their key traits and how to pick the right film matters for the best results. These films keep improving, giving industry users fresh ways to boost product quality and performance. Understanding their features and uses helps you make smart decisions for your projects and needs.

