What Is Automation in Metalized Film Manufacturing and Why Is It Important?

Automation in metalized film manufacturing means using machines and technology to run production processes with minimal human effort. Instead of workers doing every step by hand, automated systems handle tasks like coating, metalizing, and lamination with high precision and speed. This shift is not just about cutting costs; it helps meet rising quality demands and handles the complexities of modern metalized films.
Metalized film manufacturing involves three key steps:
- Coating: Applying a thin layer of adhesive or primer to the film surface.
- Vacuum metalizing: Depositing a fine metal layer, usually aluminum, onto the film in a vacuum chamber.
- Lamination: Bonding the metalized film to another substrate like plastic or paper for strength and durability.
These processes require tight control and uniformity to avoid defects like streaks or peeling. Automation excels here by providing precise control over temperature, thickness, and speed.
Core automation technologies commonly used include:
- Roll-to-roll systems: These handle large rolls of film continuously. The film unwinds on one side, passes through coating, metalizing, and lamination stations, then rewinds. This system ensures smooth, nonstop production.
- Robotic handling: Robots load, unload, and move films between steps, reducing manual labor and injury risk from handling heavy rolls or hazardous materials.
- CNC integration: Computer Numerical Control machines precisely manage coating head positions, metal thickness, and lamination pressure, controlling processes down to microns.
Several major forces drive the adoption of automation in metalized film production today:
- Supply chain resilience: Automation reduces dependency on variable manual labor. It enables reshoring and local manufacturing closer to customers, cutting delivery delays and shipping costs.
- Labor shortages and rising wages: Skilled workers in manufacturing are scarce, especially for repetitive or hazardous tasks. Automation helps fill this gap and controls labor costs.
- Stringent quality demands: Applications like snack food packaging require films with perfect metal layers for moisture and oxygen barriers to keep products fresh. Automated controls ensure this quality consistently.
Automation solves traditional challenges in metalized film manufacturing like:
- Consistency: Automated process control eliminates variations caused by shifts, operator fatigue, or manual settings. Every film receives the same metal thickness and coating every cycle.
- Speed: Automation enables continuous roll-to-roll production at higher speeds than manual or semi-manual setups, increasing throughput without quality loss.
- Safety: Automation reduces human exposure to chemical vapors and heavy lifting, improving worker health and reducing accidents.
Here is a simple comparison of manual and automated metalized film workflows:
| Workflow Aspect | Manual Process | Automated Process |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Intensity | High; many manual steps and human intervention | Low; machines handle most tasks with few operators |
| Production Speed | Limited by human handling and timing | High-speed continuous roll-to-roll processing |
| Quality Consistency | Variable; depends on operator skill and shifts | Uniform, controlled by precise sensors and controls |
| Safety | Higher risk; worker exposure to chemicals | Lower risk; robots and enclosures protect workers |
| Data Logging | Limited or manual | Automated, real-time process data for audit and trace |
Even with automation, some sectors and materials require special care. For example, metalized films used in food packaging must meet strict FDA and ASTM standards. Automation systems must integrate real-time quality checks and chemical dosing controls to stay compliant. Films designed for electronics need ultra-thin and uniform metal coats, requiring ultra-precise CNC controls and vacuum system monitoring.
Automation in metalized film manufacturing means more than just machines replacing people. It involves reorganizing production flow, selecting the best technologies for each task, and training workers to operate and maintain new systems. By doing so, manufacturers gain faster, safer, and more reliable production that meets today’s market challenges head-on.
So, what does automation in metalized film manufacturing actually entail? It means transforming complex, multi-step processes into smooth, tightly controlled workflows managed by advanced machines and software. Why is this crucial? Because metalized films must meet rising customer expectations rapidly while managing costs and labor struggles. And which steps are best for automation? High-precision coating, continuous vacuum metalizing, and lamination fit perfectly since they need accuracy, speed, and controlled environments best suited for automated solutions.
What Are the Benefits and Technical Innovations of Automating Metalized Film Production?

When we discuss automation in metalized film manufacturing, the benefits and innovations are profound. Automating metalized film production brings major improvements in speed, quality, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Let me walk you through the core advantages and some of the newest technologies changing this sector.
Increased Throughput and Continuous Flow
Automated metalized film lines can run without stopping for breaks or manual handling delays. This continuous flow leads to much higher throughput. For example, roll-to-roll automation systems enable film to move seamlessly through vacuum metalizing chambers and coating stations. The result? Much faster production rates than manual lines.
In fact, many plants report throughput increases of 30-50% after automating their metalized film lines. Continuous processing also reduces dead time, so materials are used more efficiently.
Enhanced Product Consistency and Quality Control
One of the biggest automation advantages in metalized film production is consistent quality. Automated process controls monitor parameters like coating thickness, vacuum pressure, and temperature continuously. This precision removes variations caused by human operators or shift changes.
Since product defects are reduced, scrap rates drop. Automation also enables real-time quality data logging, allowing quick responses to drift or out-of-spec conditions. This tight control ensures every meter of film meets high standards.
Reduced Operator Chemical Exposure and Ergonomic Risks
Manual metalizing processes involve contact with solvents, chemicals, and heat. Automation uses robotics and sealed systems, greatly limiting operator exposure. This improves workplace safety by cutting down chemical inhalation risks and skin contact.
Robots also handle heavy rolls and awkward lifting, relieving workers from physical strain. Automated systems reduce ergonomic injuries and fatigue, creating a healthier work environment.
Cost Savings Through Optimized Chemical and Energy Use
Automation achieves precise chemical dosing, minimizing waste of metallization agents or solvents. Heating elements and vacuum pumps operate exactly as needed, lowering energy use.
Controlled rinse cycles and heating times prevent overconsumption of utilities. These optimizations can reduce operational costs by up to 15% or more. Plus, less chemical use benefits the environment.
Advanced Sensing and Real-Time Quality Assurance
Modern lines include sensors such as laser thickness gauges, machine vision cameras, and infrared temperature probes. These give instant feedback on product quality.
Quality assurance teams can track parameters live and respond rapidly. Automated data logging aids audits and root cause analysis, supporting regulatory compliance.
Emerging Innovations Accelerating Automation
The field of metalized film automation is growing fast with several exciting tech trends:
- AI-Driven Maintenance Prediction: Machine learning algorithms analyze sensor data to forecast failures before they occur. This cuts unplanned downtime and maintenance costs.
- Adaptive Control Systems: These smart controls adjust process settings in real-time based on product feedback. They adapt to material variations automatically.
- Integration of X-Ray Inspection Methods: X-ray systems scan metalized film packaging for defects, missing components, or contaminants. They work well despite metal interference that hinders metal detectors, improving product safety.
Case Studies of Successful Automation Projects
| Company | Automation Features | Benefits Achieved |
|---|---|---|
| A Metal Film Co. | Full roll-to-roll vacuum metallizing line with robotics | 40% throughput increase, 20% chemical savings, zero safety incidents in 2 years |
| FoodPack Films | AI-based predictive maintenance and adaptive controls | 30% reduction in unplanned downtime, improved film uniformity |
| SecurePack Ltd. | X-ray inspection integration in metalized snack packaging | 50% fewer recall alerts, enhanced contaminant detection |
Environmental and Sustainability Benefits
Automation also supports sustainability goals. Reduced chemical waste lowers hazardous disposal needs. Efficient energy use cuts carbon footprints. Less scrap means fewer raw material resources consumed.
By optimizing production and minimizing rejects, manufacturers reduce environmental impact. This also improves public image and regulatory compliance.
What Operational and Cost Benefits Does Automation Bring?
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Boosted production speed | Higher throughput and continuous operation |
| Less material and chemical waste | Optimized use of chemicals and raw materials |
| Lower energy bills | Efficient use of heating and vacuum systems |
| Reduced labor costs | Fewer manual steps and labor-intensive tasks |
| Higher yield | Consistent quality and fewer defects |
What Recent Technological Innovations Support Automation?
- Artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance
- Adaptive closed-loop control systems for real-time adjustments
- Advanced X-ray inspection for metalized packaging
- Robotics handling to replace repetitive and dangerous tasks
- Sophisticated sensing technologies like laser thickness gauges
How Does Automation Improve Safety and Environmental Sustainability?
- Limits operator contact with chemicals and heat
- Reduces ergonomic injuries by automating heavy lifting and handling
- Cuts down energy and chemical consumption
- Minimizes waste and scrap
- Enhances monitoring to detect leaks or hazards early
Automation in metalized film manufacturing is not just a way to save money or speed things up. It is a key step towards safer working conditions, consistent product quality, and greener production. With emerging innovations, the future looks even brighter for this sector.
What Are Implementation Challenges and Best Practices for Automation in Metalized Film Manufacturing?
When we discuss automation in metalized film manufacturing, we must also explore the challenges that come with it and the best ways to overcome them. Automation brings many advantages, but implementing it in metalized film lines can be complex.
Common Challenges in Metalized Film Manufacturing Automation
One major challenge is the upfront investment required. Automated systems, especially those tailored to metalized film production, demand significant capital. The equipment often needs customization due to the specific nature of metalized film processes, such as vacuum metalizing or lamination. Off-the-shelf solutions rarely fit perfectly, meaning engineers and manufacturers must spend extra time and money to adapt systems.
Another obstacle is workflow complexity. Metalized film manufacturing involves many delicate steps. Before automation, manufacturers must map out manual processes thoroughly. This prevents automation from amplifying inefficiencies or errors already present in the line.
Additionally, many companies face workforce resistance. Automating long-standing manual tasks can raise fears about job security. Without clear communication and training, workers might resist changes or feel unprepared. This can slow down or even derail automation efforts.
Importance of Workflow Re-Engineering and Manual Process Mapping
Before adding automation, it’s vital to re-engineer workflows and critically assess every step. Manual operations often include redundancies or hidden bottlenecks. Mapping each task helps identify:
- Where delays occur
- Which steps add little value or create waste
- Safety risks or ergonomic issues
Only after these insights can automation be integrated successfully. Skipping this step risks building inefficient automated systems that are expensive and hard to maintain.
Example: A metalized film packaging plant found that by mapping manual film transfer points, they could eliminate three handling steps before automation. This optimized uptime by 15% and cut operator error rates drastically.
Choosing Suitable Automation Technology
Selecting the right automation tools is key. Options include:
| Technology Type | Best Use Case |
|---|---|
| Industrial Robots | High-volume, repetitive tasks with uniform parts |
| Collaborative Robots (Cobots) | Flexible handling of varying batch sizes and moderate complexity |
| Pick-and-Place Devices | Simple, fast movement of light components |
For metalized films, where delicate handling and precision are needed, cobots often shine. They offer adaptability, safety near humans, and can manage variable production runs. However, if volumes are large and parts consistent, traditional robots may offer better cost savings.
The Role of Automation Champions and Cross-Functional Teams
One best practice I emphasize is appointing empowered automation champions. These individuals are experts who:
- Know metalized film processes deeply
- Bridge gaps between engineering, production, and planning
- Lead the automation project with clear, realistic goals
Their leadership is crucial. Automation often involves multiple departments, so forming cross-functional teams ensures alignment and smooth communication.
Case study: A firm deploying metalized film automation saw faster adoption after naming a champion to oversee integration. The champion coordinated vendors, scheduled training, and promptly addressed unforeseen issues.
Training and Upskilling Operators and Maintenance Staff
Automation introduces new interfaces and safety protocols. Training is not just about teaching operators how to push buttons. It’s about building troubleshooting skills, safety awareness, and maintenance know-how.
Hands-on training should cover:
- System controls and user interfaces
- Safety features and emergency stops
- Routine checks and preventative maintenance
- Troubleshooting basic faults
This empowers workers to handle new systems confidently and cuts costly downtime.
Preventive Maintenance and Backup Strategies
Continuous operation is essential for metalized film plants, where downtime means lost revenue and missed orders. Automated systems often include many electromechanical parts that need regular care.
Implementing preventive maintenance schedules is a best practice. This includes:
- Regular inspection of moving parts and sensors
- Scheduled software updates
- Calibration of equipment to maintain precision
- Backup systems or fallback manual processes
These strategies ensure high uptime and avoid unscheduled halts that disrupt customer delivery.
Integration With Quality Assurance and Regulatory Compliance
Metalized film manufacturing is subject to quality and regulatory standards like ASTM A967 for passivation and hygiene rules for food packaging. Automation must integrate seamlessly with existing quality assurance (QA) systems.
This can be done by:
- Automating data logging and reporting for process parameters
- Linking inspection outputs with QA databases
- Ensuring traceability for audits
Such integration simplifies regulatory compliance, reduces human error in documentation, and speeds up audits.
Overcoming Workforce Resistance Through Communication and Development
Resistance to automation usually comes from fear of job loss or lack of skills. To overcome this:
- Communicate openly about goals and benefits
- Emphasize how automation removes tedious or dangerous jobs
- Highlight upskilling opportunities to advance worker careers
- Involve workers early in planning and testing phases
This builds trust and a collaborative mindset rather than conflict.
Methods for Continuous Monitoring, Documentation, and Scaling
Finally, successful automation requires ongoing effort beyond installation. Implement:
- Continuous monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) such as uptime, quality yield, and throughput
- Document lessons learned, issues, and fixes in a central knowledge base
- Use data to refine and improve the automated system regularly
- Develop a roadmap to scale automation to other lines or plants
This approach helps manufacturers maximize ROI, keep up with technological advances, and stay competitive.
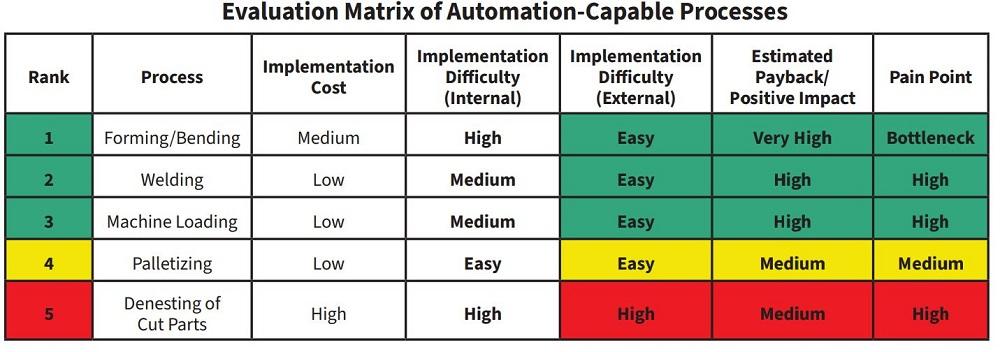
In brief: Metalized film automation requires proper planning, choosing the right technology, managing change, and ongoing support. Automation champions and cross-functional teams, together with training and preventive care, make the difference between costly experiments and smooth transformations. With the right approach, automation will unlock efficiency, safety, and higher product quality in metalized film manufacturing.
FAQs about Discuss automation in metalized film manufacturing:
What is automation in metalized film manufacturing and why is it important?
Automation in metalized film manufacturing means using machines and technology to run production processes with minimal human effort, ensuring precise control over coating, metalizing, and lamination steps to meet quality demands and address labor challenges.
What are the benefits and technical innovations of automating metalized film production?
The benefits of automating metalized film production include increased throughput, consistent product quality, improved safety by reducing chemical exposure and ergonomic risks, cost savings from optimized chemical and energy use, and advanced sensing technologies for real-time quality assurance.
What operational and cost benefits does automation bring to metalized film manufacturing?
Automation boosts production speed, reduces material and chemical waste, lowers energy consumption, decreases labor costs, and improves yield through consistent quality and fewer defects.
What challenges are involved in implementing automation in metalized film manufacturing and how can they be overcome?
Challenges include high upfront investment, workflow complexity, and workforce resistance; they can be overcome by re-engineering workflows, choosing suitable automation technologies, appointing automation champions, providing thorough training, and fostering open communication with workers.
How does automation improve safety and environmental sustainability in metalized film manufacturing?
Automation limits operator contact with hazardous chemicals and heat, reduces ergonomic injuries, cuts down on energy and chemical consumption, minimizes waste and scrap, and enhances monitoring to detect hazards early, supporting a safer and greener production environment
Automation is changing metalized film manufacturing, making it faster and safer. It helps keep product quality high while cutting costs and risks. We looked at key steps and tools, like robotic arms and sensors, that make this possible. We also saw challenges, like upfront costs and staff training, but smart planning solves these. In the end, automation is no longer optional—it’s essential for efficient and reliable metalized film production today.

