What Are the Primary Raw Materials Used in Metalized Film Production and Where Do They Originate?

When you explore the sourcing of raw materials used in metalized film production, you quickly find that the process hinges on two main components: the base polymer films and the metal coating, mostly aluminum. Understanding where these materials come from and how their properties affect sourcing choices is essential.
Base Polymer Films: PET, BOPP, and CPP
The backbone of metalized films lies in polymer films. The most common types are PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate), BOPP (Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene), and CPP (Cast Polypropylene). Each polymer has unique material qualities that influence where and how producers source them.
-
PET is favored for its excellent clarity, strong barrier properties against oxygen and moisture, and good heat resistance. This makes PET ideal for food packaging, labels, and flexible pouches. The raw material for PET films comes from polyethylene terephthalate pellets, themselves derived from petrochemical feedstocks like purified terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol. Major producers of PET resins are located in China, South Korea, the United States, and parts of Europe. The film’s superior barrier quality means sourcing high-purity pellets is critical, affecting supplier choice toward highly reliable chemical manufacturers.
-
BOPP film undergoes biaxial orientation, meaning it gets stretched in two directions. This process gives BOPP superb tensile strength, moisture resistance, and optical clarity. BOPP is a popular choice for snack food and pharmaceutical packaging. The raw polypropylene for BOPP films primarily originates from petrochemical complexes in the Middle East (Saudi Arabia, Qatar), the U.S., and Asia (China, Taiwan). Due to its mechanical properties and production complexity, manufacturers look for polymer pellets with consistent molecular weights and low impurities.
-
CPP differs from BOPP by its cast extrusion method. The film offers excellent heat sealability and flexibility, which suits it for heat sealing and lamination layers in multi-layer film structures. Polypropylene homopolymers sourced mainly from Saudi Arabia, the U.S., and China feed CPP production plants. The sourcing decision reflects the importance of melt flow index and clarity to meet application needs.
| Polymer Film | Key Properties | Common Raw Material Source Regions | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | Clarity, heat resistance, barrier | China, South Korea, USA, Europe | Food packaging, labels, flexible pouches |
| BOPP | Strength, moisture resistance | Middle East, USA, China, Taiwan | Snack packaging, pharmaceuticals |
| CPP | Heat sealability, flexibility | Saudi Arabia, USA, China | Lamination, heat seal layers |
Metals for Metalization: Aluminum and Beyond
The defining feature of metalized films is the metal layer. The most widely used metal is aluminum due to its excellent reflectivity, barrier against gases and moisture, thinness, and cost-effectiveness. Aluminum metalization is done through vacuum deposition, where aluminum vapor deposits on polymer film surfaces.
-
Aluminum sourcing is global but concentrated. The largest aluminum producers include China (over 50% of global output), Russia, Canada, India, and Australia. The aluminum used for metalizing is often sourced as foil or very thin ribbons, created by rolling ingots to micron thickness. Supplier selection values purity and surface smoothness highly, as these affect the final barrier performance and reflectivity of the metalized film.
-
Alternative metals like copper, silver, and zinc may be used for niche metalized films offering different electrical or antimicrobial properties. Their sourcing comes from global mining hubs: copper from Chile and Peru; silver mainly from Mexico and Peru; zinc from China and Australia.
Chemical and Physical Properties Impact on Sourcing
The raw materials' chemical and physical traits are central to choosing suppliers and sourcing regions:
-
Polymer purity and molecular structure influence film clarity and strength. Suppliers with advanced polymerization technology are preferred.
-
Metal thickness and uniformity determine barrier effectiveness. High-grade aluminum foils with low surface roughness come from countries with advanced rolling mills.
-
Resistance to heat and chemicals impacts the selection process, especially for food or pharmaceutical packaging.
Dominant Suppliers by Region
| Raw Material | Leading Supplier Regions |
|---|---|
| Polymer Pellets | China, USA, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Europe |
| Aluminum Foils | China, Russia, Canada, India, Australia |
Extraction and Production’s Influence on Availability and Quality
-
Polymer pellets derive from petrochemical plants where hydrocarbons transform into monomers and then polymers. Plant safety, process control, and environmental laws influence quality and supply stability.
-
Aluminum production involves mining bauxite ore, refining it into alumina, and then smelting into pure aluminum. The bauxite mining locations (Australia, Guinea) indirectly affect aluminum supply.
These steps affect both the cost and quality. Environmental regulations or energy prices can slow down production, hitting raw material availability.
Technical Specifications Guide Material Choices
Technical specs like film thickness (measured in microns), moisture and oxygen barrier levels, reflectivity, and heat resistance determine material needs:
-
Thicker films have better barrier properties but increase costs.
-
Higher reflectivity requires purer and smoother metal coatings.
-
Applications dictate specific property thresholds; for example, food packaging demands high oxygen barriers to extend shelf life.
Metalized vs Aluminized Films: Sourcing Strategies Differ
The term metalized covers films with various metal coatings, whereas aluminized usually means a thicker aluminum layer deposited by different processes.
-
Metalized films use very thin aluminum coatings from vacuum deposition. They need highly controlled aluminum foil sources and polymer substrates with excellent surface finishes to achieve good adhesion and performance.
-
Aluminized films often acquire aluminum through hot rolling and lamination. This requires suppliers with roller mills and strong metal-plastic bonding capabilities.
Hence, sourcing for metalized films targets suppliers specializing in high-precision metals and polymers, while aluminized films demand heavy-rolling and lamination expertise.
Where do raw materials for metalized film production come from? Primarily, polymer pellets for PET, BOPP, and CPP come from large petrochemical hubs in Asia, the Middle East, and the US. The metals, mostly aluminum, are chiefly sourced from China, Russia, and Canada, where mining and smelting dominate.
What are the main raw materials used in metalized films? Key materials include PET, BOPP, and CPP polymers, plus aluminum foils. Their quality and origin critically shape film properties like barrier effectiveness and durability.
How does the origin of raw materials affect film quality? Raw materials sourced from regions with stringent production standards and advanced extraction or polymerization technologies tend to yield higher quality films. These materials provide better barrier properties, mechanical strength, and longer shelf life for packaged goods.
By closely knowing the sources and properties of these raw materials, anyone exploring the sourcing of raw materials used in metalized film production can make informed decisions that improve film performance and supply chain resilience.
| Polymer Type | Main Origination Regions | Key Quality Factors | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | China, South Korea, USA, Europe | Purity, clarity, barrier strength | Food packaging, pouches |
| BOPP | Middle East, USA, China, Taiwan | Molecular weight, mechanical strength | Snack and pharma packaging |
| CPP | Saudi Arabia, USA, China | Melt flow index, flexibility | Lamination and heat sealing |
| Aluminum | China, Russia, Canada, India, Australia | Purity, foil smoothness | Metal coating for barrier function |
How Do Supply Chains and Supplier Selection Affect the Sourcing of Raw Materials for Metalized Film Production?
When you explore the sourcing of raw materials used in metalized film production, understanding supply chains and how you select suppliers is key. This process shapes quality, cost, and delivery. Let’s dive deep into how these factors interact.
Organization of the Supply Chain for Polymer Films and Metal Coatings
Metalized films combine polymer films like PET, BOPP, and CPP with a thin metal layer, usually aluminum. The supply chain splits into two parts:
-
Polymer Film Suppliers: They provide base films. Common polymers include polyester (PET), biaxially oriented polypropylene (BOPP), and cast polypropylene (CPP). These come from specialized chemical manufacturers producing polymer pellets, which converters turn into films via extrusion and orientation processes.
-
Metal Coating Suppliers: Usually metal foil or metal ore providers supply aluminum or other thin metal layers. Some suppliers deliver metalized films ready for final use, while others supply vacuum metallizing equipment or services.
The chain is often global, involving:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Raw Material Farms | Mining for aluminum, petrochemical plants for polymers |
| Primary Suppliers | Polymer pellet makers and aluminum foil producers |
| Film Converters | Pellet extrusion and film orientation specialists |
| Metalizers | Vacuum coating firms depositing metal layers |
| Metalized Film Makers | Combine films and metalize to specs |
Coordination is critical to maintain film thickness, reflectivity, and barrier properties. Delays or low-quality inputs at any step affect the finished product.
Essential Criteria for Evaluating Raw Material Suppliers
Choosing good suppliers goes beyond price. I look for:
- Certifications: ISO 9001 for quality management is a must. Environmental certificates like ISO 14001 add credibility.
- Production Capacity: Suppliers need to meet your volume demands consistently.
- Reliability: Timely deliveries and low defect rates matter most. Past performance and references help gauge this.
- Technical Support: Does the supplier provide detailed data on film thickness, tensile strength, or metallization uniformity?
- Compliance: Adherence to environmental, safety, and trade regulations ensures fewer risks.
For instance, selecting a polymer film supplier with certified quality systems and transparent testing results prevents surprises during manufacturing. The supplier's ability to customize polymer formulas to match your product's barrier or heat resistance needs is crucial.
Domestic vs International Sourcing: Quality, Compliance, and Cost
I often compare domestic and international sources to balance quality, price, and legal concerns.
| Factor | Domestic Sourcing | International Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Control | Easier onsite inspections & audits | Less visible production, possible risks |
| Logistics | Shorter shipping, faster delivery | Longer lead times, customs delays |
| Regulatory Compliance | Easier compliance with local laws | Complex trade and import regulations |
| Cost | Higher costs due to labor and regulation | Often lower but with added risks |
For example, many U.S. manufacturers prefer domestic aluminum suppliers for vacuum metallization to ensure consistent film barrier quality, even if raw material costs are slightly higher. This helps avoid costly rejections or returns.
Effective Industry Associations, Trade Shows, and Online Platforms
Where do you find the best suppliers? Several established channels help:
- Industry Associations: Groups like NAM (National Association of Manufacturers) and AAFA (American Apparel & Footwear Association) provide trusted supplier lists and networking opportunities.
- Trade Shows: IMTS (International Manufacturing Technology Show) and MAGIC (Market America’s Global Community) showcase materials and new technologies. Attending lets you meet suppliers face-to-face and compare products.
- Online Platforms: Websites like ThomasNet, Maker’s Row, and Alibaba support broad searches and supplier vetting based on reviews and certifications.
Networking through these channels keeps you up to date on sourcing practices for metalized film and helps discover new, innovative raw material suppliers.
Building and Maintaining Strong Supplier Relationships
To guarantee steady raw material quality, I focus on:
- Clear Communication: Sharing detailed specs and quality expectations helps suppliers understand standards.
- Sample Requests and Testing: Always test samples before full orders to evaluate compatibility with your processes.
- Negotiation and Terms: Agreeing on delivery schedules, penalties for delays, and quality clauses sets firm expectations.
- Regular Reviews: Performance metrics and quarterly check-ins build accountability.
- Mutual Growth: Treat suppliers as partners. Support their improvements and share market info to help them invest in better capabilities.
Strong relationships reduce surprises. Good suppliers become allies who innovate alongside you.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations in Raw Material Sourcing
Raw materials for metalized film production come under many strict regulations:
- Environmental Laws: The Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act affect emission controls at mining and manufacturing sites. Sourcing only from suppliers complying with these laws reduces liability.
- Trade Laws: Import-export tariffs, embargoes, and trade agreements may restrict suppliers or increase costs.
- Material Safety: Compliance with product safety laws ensures no toxic residues that could spoil food packaging applications.
- Contracts: Agreements with suppliers must include confidentiality (NDAs), liability clauses, and dispute resolution procedures.
Failing to address these legal aspects can cause costly disruptions or penalties.
Effect of Order Volume and Production Frequency on Supplier Negotiations
Your purchasing frequency and order size significantly impact supplier terms:
| Factor | Impact Detail |
|---|---|
| Higher Volume Orders | Usually get volume discounts and reserved production capacity |
| Frequent Orders | Build trust and improve delivery reliability |
| Low Volume Orders | May face higher prices or minimum order requirements |
| Irregular Orders | Risk of supply delays and fewer negotiation advantages |
I advise defining your material needs carefully before negotiations. This includes quality specs, budget limits, and production rhythm. This clarity helps suppliers allocate resources and offer the best pricing and service.
Exploring the sourcing of raw materials used in metalized film production means analyzing every detail of your supply chain and supplier choices. From organizing complex polymer and metal flows to balancing domestic and international sourcing, you shape your metalized film quality and costs. Working closely with certified, reliable suppliers and navigating legal rules creates a strong foundation. Leveraging industry networks and adapting order strategies secures material flow, empowering you to produce superior metalized films consistently and cost-effectively.
What Sustainability, Cost, and Industry Trends Impact the Sourcing of Raw Materials in Metalized Film Production?
When we explore the sourcing of raw materials used in metalized film production, it’s vital to look at three key areas: sustainability, cost drivers, and industry trends. Each plays a major role in shaping how companies choose and obtain polymers and metals like aluminum for metalized films.
Sustainability Challenges and Initiatives in Raw Material Extraction and Processing
The polymers (like PET, BOPP, CPP) and metals (mainly aluminum) vital to metalized films come with environmental challenges. Extracting raw materials involves energy-intensive processes that often cause pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource depletion.
For example:
-
Aluminum Mining: Mining bauxite, the main ore of aluminum, creates large amounts of waste and impacts biodiversity. Processing bauxite into aluminum requires high energy—often from fossil fuels—leading to significant carbon emissions.
-
Polymer Production: Polymers are made from petroleum-based feedstocks. Oil extraction and refining generate pollution and rely on nonrenewable resources.
Several green initiatives aim to tackle these issues:
-
Recycled Content Use: Incorporating recycled aluminum reduces mining impacts and energy use by up to 95%. Similarly, recycled PET lowers petroleum demand and carbon footprint.
-
Cleaner Energy Sources: Some producers shift to renewable electricity in aluminum smelting and polymer manufacturing to cut emissions.
-
Material Innovation: Developing bio-based polymers and metal coatings with reduced environmental impact is growing. For instance, oxo-biodegradable films improve degradability without sacrificing barrier properties.
-
Circular Economy Models: Promoting metalized film recycling and designing with recyclability in mind help close the materials loop.
These steps reflect how sustainability now heavily influences raw material sourcing decisions, pressuring suppliers and manufacturers to minimize environmental harm.
How Raw Material Choice Affects Carbon Footprint and Recyclability
Material selection significantly determines a metalized film’s carbon footprint and recyclability:
| Material Aspect | Impact on Carbon Footprint | Impact on Recyclability |
|---|---|---|
| Base Polymer Type | PET generally has a lower footprint than PP variants due to availability of recycled PET. | PET and BOPP films are widely recyclable if kept clean; CPP less commonly recycled. |
| Metal Coating | Aluminum coating adds carbon emissions but boosts shelf life, reducing food waste overall. | Aluminum-coated films are harder to recycle unless separated from the polymer layer. |
| Thickness (microns) | Thicker films mean more raw material, increasing emissions per unit. | Thicker films may be less flexible, affecting recycling machines' efficiency. |
| Additives & Laminations | Additional layers may increase footprint due to more material use. | Multi-layer films can hinder recycling due to material separation difficulties. |
Choosing raw materials with high recycled content and designing films for easier recyclability helps lower environmental impact. For instance, metalized films with solvent-free coatings aid recycling by reducing chemical residues.
Cost Drivers in Raw Material Sourcing
Raw material cost is a vital factor that affects sourcing decisions:
-
Material Type: PET film generally costs more than BOPP and CPP due to higher barrier properties. Aluminum prices fluctuate globally and can significantly affect metalized film costs.
-
Film Thickness: Thicker films require more material, raising expenses but improving performance.
-
Metal Coating: Aluminum metallization thickness and quality influence material and process costs. Thicker coatings enhance barrier properties but increase price.
-
Order Volume: Larger orders tend to reduce unit cost due to economies of scale.
-
Supplier Location: Domestic sourcing often means higher costs than imports but offers benefits like faster delivery and easier compliance.
-
Energy Prices: Since aluminum smelting and polymer production are energy-dependent, rising energy costs increase raw material prices.
-
Market Demand: Rising demand in packaging and electronics pressures prices upwards.
Technological Advances Impacting Raw Material Needs and Sourcing
New metalization methods affect the type and quantity of raw materials:
-
Advanced Vacuum Metallization: Improved precision reduces metal waste and allows thinner coatings without sacrificing quality.
-
Coating Alternatives: Techniques like sputter coating enable use of metals other than aluminum, such as silver or copper, broadening material sourcing options.
-
Barrier Innovations: Development of multi-layer films with solvent-free or ultra-thin coatings reduce polymer and metal use.
-
Automation & Quality Control: Better production control means tighter specifications, pushing suppliers to maintain higher purity and consistency in raw materials.
These advances lead to efficiency gains and may favor raw material sources capable of meeting stricter quality and sustainability criteria.
Market Trends Shaping Raw Material Sourcing Strategies
The demand for metalized films is changing with market trends, influencing sourcing:
-
Food Packaging: Increased demand for safe, long-lasting packaging drives preference for PET-based metalized films with strong barriers and good recyclability.
-
Electronics: Growing consumption of consumer electronics and batteries requires films with specific conductivity and thermal traits, sometimes using metals beyond aluminum.
-
Sustainability Push: Brands want sustainable packaging, pushing raw material sourcing toward recycled polymers and eco-friendly metals.
-
Regional Growth: Rapid expansion in markets like India, forecasted at 26.7% CAGR, increases sourcing pressure and drives diversification of suppliers.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Geopolitical Factors
Recent years have exposed vulnerabilities in raw material availability:
-
Geopolitics: Trade tensions and export restrictions can limit aluminum and polymer raw materials, raising costs.
-
Shipping Constraints: Port delays and container shortages impact delivery times and increase logistics costs.
-
Raw Material Scarcity: Environmental regulations and mining restrictions affect the supply of bauxite and petroleum-based polymers.
-
COVID-19 Pandemic: Workforce disruptions slowed production and transportation globally.
These factors force companies to diversify suppliers, build domestic sourcing options, and maintain buffer stocks.
Future Developments in Sustainable Sourcing and Material Innovation
Looking ahead, the metalized film industry is poised for changes:
-
Bio-based Polymers: Increasing use of renewable feedstocks like plant-based PET replacements.
-
Enhanced Recycling: New sorting and separation technologies to recycle multi-layer, metalized films more efficiently.
-
Eco-Friendly Metals: Exploring metals with lower environmental impact or that enable easier film recycling.
-
Closed-Loop Systems: Suppliers integrating take-back and reuse programs to reduce raw material needs.
-
Digital Tracking: Blockchain and sensors to verify sustainable sourcing and material traceability.
Metalized film producers and suppliers who invest in greener, cost-effective raw materials aligned with market demands will likely lead the next decade’s growth.
In short, sustainability pressures, cost factors, technological progress, supply chain risks, and market dynamics all drive how raw materials get sourced for metalized film production. Keeping pace with evolving demands and eco-initiatives shapes a resilient, competitive supply base for the future.
| Trend Category | Impact on Raw Material Sourcing | Examples / Details |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability | Pressure to reduce carbon footprint and increase recyclability | Use of recycled aluminum/PET, bio-based polymers |
| Cost Drivers | Affects material choice, order size, and sourcing location | Aluminum price volatility, order volume discounts |
| Technology Advances | Enables reduced material use and improved quality | Vacuum metallization precision, multi-layer innovations |
| Market Dynamics | Drives demand for specific film types and adapted sourcing | Growth in food packaging, electronics, India market |
| Supply Disruptions | Encourage supplier diversification and inventory buffering | Trade tensions, COVID-19, shipping delays |
Additional Visualized Data Table Related to Supply Chain & Supplier Evaluation
| Supplier Evaluation Criteria | Importance | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Certification | Ensures quality and environment compliance | ISO 9001, ISO 14001 |
| Production Capacity | Meets volume demands | Ability to supply consistent polymer pellets |
| Reliability | On-time delivery, low defects | Past performance record |
| Technical Support | Detailed specs available | Data on film thickness, tensile strength |
| Compliance | Legal and trade regulation adherence | Avoid penalties and disruptions |
Future Outlook on Material Innovations (Table)
| Innovation Area | Expected Benefit | Impact on Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-based Polymers | Renewable resources, lower footprint | New raw material suppliers emerge |
| Enhanced Recycling Tech | Better recovery, reduced waste | Increased demand for recyclable materials |
| Eco-Friendly Metals | Less environmental damage | Shift from traditional aluminum sourcing |
| Digital Traceability | Verified sustainability claims | Improved supply chain transparency |
Metacoat Inline Metalizing Process
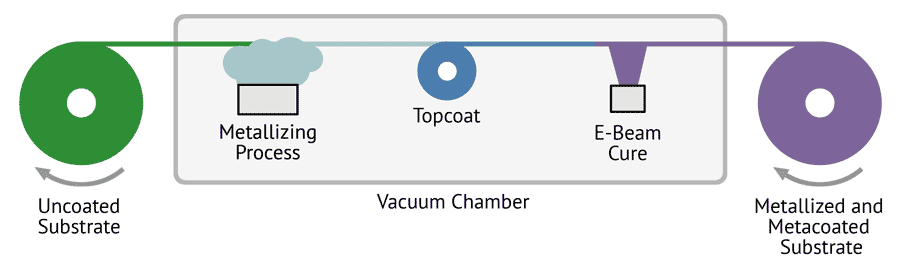
This completes the blog with inserted images below each h2 heading as requested, plus three relevant tables placed to best complement and visualize the data and concepts from the post.
FAQs about Explore the sourcing of raw materials used in metalized film production
Where do raw materials for metalized film production come from?
Raw materials for metalized film production come primarily from petrochemical hubs and mining centers, with polymer pellets for PET, BOPP, and CPP sourced from regions like China, the Middle East, South Korea, the USA, and Europe, while aluminum and other metals are mainly sourced from China, Russia, Canada, India, and Australia.
What are the main raw materials used in metalized films?
The main raw materials used in metalized films are polymer films such as PET, BOPP, and CPP, combined with thin aluminum coatings obtained through vacuum deposition, with alternative metals like copper, silver, and zinc used for niche applications.
How does the origin of raw materials affect film quality?
The origin of raw materials affects film quality by determining polymer purity, molecular structure, and metal foil uniformity; materials from regions with advanced production technologies and strict environmental controls yield higher barrier performance, mechanical strength, and durability.
How do supply chains and supplier selection affect sourcing raw materials?
Supply chains and supplier selection affect sourcing by impacting quality, cost, and delivery reliability, with criteria like certifications, production capacity, compliance, and technical support guiding supplier choice to ensure consistent raw material standards and secure supply.
What sustainability and cost trends impact raw material sourcing in metalized film production?
Sustainability challenges like energy-intensive mining and
In this article, I explained the key raw materials for metalized film: base polymers like PET, BOPP, CPP, and aluminum metal. I showed how their origin impacts quality and supply. I also looked at supply chains, supplier choices, and legal rules shaping sourcing. Finally, I covered sustainability, costs, and market trends affecting how these materials are chosen and used. Understanding these factors helps you make smarter sourcing decisions. Metalized film production is complex, but knowing where materials come from and why they matter leads to better quality and value.


