What Is Automation in Metalized Film Manufacturing and Why Is It Important?
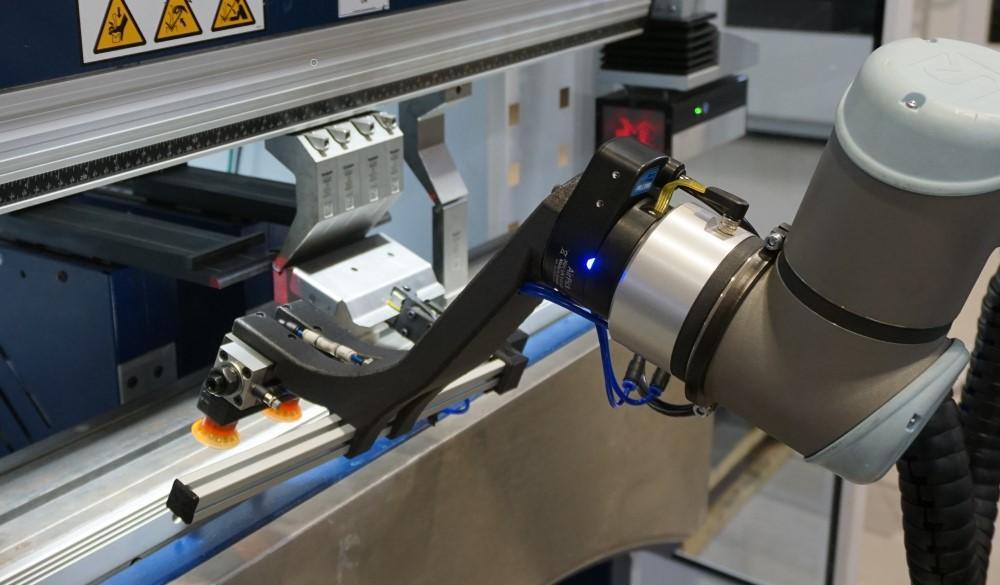

Automation in metalized film manufacturing means using machines and technology to control and run production processes with minimal human help. Instead of relying on people for repetitive or complex tasks, automation uses computers, robots, and other equipment to handle metalizing, coating, cutting, and packaging of films. This shift improves speed, accuracy, and safety across the factory.
What Defines Automation in Metalized Film Manufacturing?
Automation in metalized film production spans several processes. It includes the use of robotics and automated machinery that apply thin metal layers to plastic or paper films. These machines operate using software controls to coat films uniformly and maintain precise thickness throughout long runs. Automation also covers handling steps like unwinding rolls, straightening, cutting, and sealing films without manual intervention. Sensors and cameras continuously check film quality, catching defects early.
Key traits that define automation here are:
- Continuous operation: Machines run 24/7 with minimal downtime.
- Precision control: Automated systems keep metal coating thickness within tight limits.
- Real-time monitoring: Sensors track process variables like temperature, line speed, and coating quality.
- Data recording: Electronic logs support quality assurance and traceability.
Key Machinery and Technologies Used for Automation
Metalized film automation relies on several cutting-edge machines and tech solutions. These include:
| Machine / Technology | Role in Automation |
|---|---|
| Roll-to-roll handling systems | Move film continuously through coating stations |
| Vacuum metallizing chambers | Deposit uniform metal layers via vapor deposition |
| Automated slitters & rewinders | Cut metalized film into desired widths and rewind by roll |
| CNC bending and feeding systems | Precisely shape films or related metal parts |
| Industrial robots & cobots | Load/unload rolls, package films, maintain equipment |
| Sensors and machine vision | Detect film defects and measure coating thickness |
| Advanced software platforms | Control process variables and collect data |
These technologies work together to boost throughput while maintaining strict quality standards. For example, a roll-to-roll vacuum metallizer efficiently applies a metal coating, while a vision inspection system checks for pinholes or inconsistencies in real time.
Addressing Skilled Labor Shortages and Supply Chain Issues
The metalized film sector faces a shrinking skilled workforce, rising wages, and supply chain disruptions. Automation helps tackle these problems in several ways:
- Less dependence on manual labor: Automated machinery does the work that required experienced operators, easing staffing challenges.
- Upskilling opportunities: Workers focus on maintenance, programming, and quality control, increasing their value and career paths.
- Supply chain resilience: Automated inventory and production scheduling adapt faster to raw material delays.
- Consistent output despite variability: Unlike humans, machines avoid fatigue or error, ensuring steady production levels.
Upskilling workers to run and support automation keeps the company strong while reducing risks from labor shortages or supply interruptions.
Cost and Efficiency Benefits of Automation
Automation yields clear financial benefits but also transforms workflows for maximum efficiency:
- Lower operating costs: Reduced labor hours and optimized use of expensive metals and chemicals.
- Higher throughput: Machines run faster and longer with less downtime, meeting tight deadlines.
- Less waste: Automated dosing systems minimize coating overuse or scrap film.
- Reduced lead times: Faster setup and changeover speeds respond better to customer needs.
- Increased revenue: Greater capacity and product consistency improve customer trust and expand orders.
One case study showed automating metallizing lines cut production time by 30% and reduced material waste by 12%, improving overall profit margins.
Improving Product Quality and Consistency
Automated metalized film lines produce more uniform, higher-quality films. Machine precision avoids human errors such as uneven metal layers or defects caused by fatigue. Real-time monitoring systems alert operators to changes in line speed or coating thickness before defects appear. Electronic documentation of every batch aids traceability and supports strict regulatory compliance for packaging films.
Table: Product Quality Improvements Due to Automation
| Quality Metric | Before Automation | After Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Thickness Variation | ±15% | ±3% |
| Defect Rate (pinholes, scratches) | 5 per 1000 m² | 0.5 per 1000 m² |
| Batch-to-batch Consistency | Moderate | High |
| Documentation Completeness | Manual logs | Digital records |
This improved quality ensures end users receive metalized films that protect contents longer, resist moisture and oxygen, and maintain aesthetic appeal.
Enhancing Workplace Safety with Automation
Metalized film manufacturing involves hazardous chemicals, heavy lifting, and repetitive tasks. Automation makes factories safer by:
- Reducing operator exposure to chemical vapors and solvents.
- Eliminating manual handling of large heavy film rolls.
- Using robots to perform dangerous tasks like metal coating or packaging.
- Providing emergency stop functions and safety interlocks on machines.
- Enabling consistent process control to avoid unsafe conditions caused by human error.
Safety cost savings can be as significant as labor cost savings and are vital to project budgets. Automation also reduces injury-related absences and improves employee morale by delivering a safer work environment.
Final Thoughts on Automation’s Importance
Automation in metalized film manufacturing is no longer optional. It answers critical industry challenges: labor gaps, rising costs, and quality demands. With the right machines, skilled staff, and management, automation delivers lower costs, higher output, better product quality, and a safer workplace. For companies seeking to remain competitive in the fast-evolving packaging market, embracing automation is key.
How Is Automation Implemented in Metalized Film Manufacturing Processes?

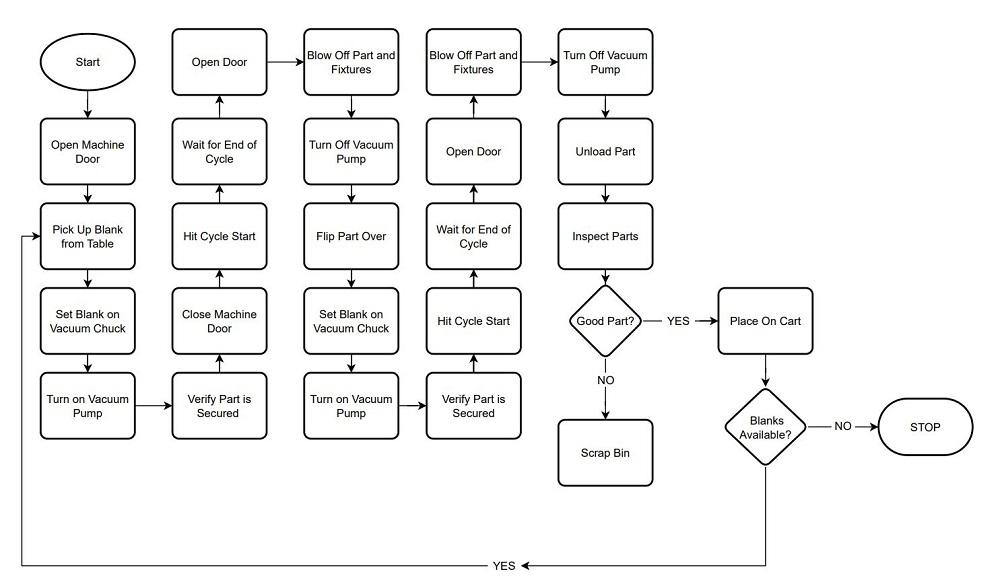
Automation processes in metalized film manufacturing have become vital to address challenges such as labor shortages, rising wages, and supply chain disruptions. Implementing automation requires a strategic approach, involving machinery choices, process redesign, safety planning, and team training. Let me walk you through how automation takes shape in this sector.
Common Automation Types Used in Metalized Film Manufacturing
Automation in metalized film production includes a range of technologies suited to different tasks and production scales:
- Industrial Robots: These are heavy-duty machines programmed for high-volume, uniform metalized film tasks. They handle film coating, cutting, and stacking with great precision. For example, a robot arm can load and unload rolls consistently over long shifts.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots are flexible and work alongside humans. They fit smaller production scales or variable jobs, such as quality inspection or spot coating. Cobots can easily switch between tasks without extensive reprogramming.
- Simple Automation Devices: These include sensors, conveyors, automated feeders, and pneumatic actuators used for repetitive, low-variation tasks. They reduce manual intervention in roll feeding and unwind/rewind operations.
Choosing between these options depends on product volume, variation, and business impact. High-volume wheel-like stainless steel passivation lines, for example, use industrial robots for continuous operation. Smaller, custom metalized film batches benefit more from cobots or simple automation devices.
Role of Roll-to-Roll Handling and Continuous Processing Technologies
Continuous processing allows metalized films to move from coating to finish lines without interruption. Roll-to-roll (R2R) technology is a backbone of automation here, supporting highly efficient and scalable metalized film manufacturing.
- Unwinding and Rewinding: Automated tension controls keep the film tight and aligned during processing, reducing material waste by up to 15% compared to manual methods.
- Film Transport: Conveyor rollers and robotic handlers move rolls seamlessly through vacuum metalizing, coating, and drying stations.
- Inline Inspection: Sensors scan films in real-time to detect defects like pinholes or coating unevenness. Data triggers automatic adjustments or roll rejection without stopping the line.
This continuous approach minimizes idle time and operator involvement, boosting throughput and quality consistency.
Steps to Re-engineer Manual Processes for Automation Readiness
Before automation can be integrated, existing manual metalized film processes must be mapped and optimized:
- Process Mapping: Document current workflows, noting inputs, machine parameters, defects, and bottlenecks.
- Stability Checking: Analyze if raw materials and operating conditions are consistent enough to automate. Variability here can cause automation systems to fail.
- Simplification: Remove unnecessary steps or redundancies. Streamlined tasks are easier to mechanize.
- Standardization: Set clear quality and safety standards for each process stage.
- Equipment Assessment: Verify whether current machines are compatible with automation or need upgrades.
- Automation Ranking: Prioritize processes for automation based on impact, safety, difficulty, and operator availability. Initially, target high-impact or high-risk tasks.
This preparation ensures smooth integration, reducing costly redesigns after automation deployment.
Designating Automation Champions and Their Role
A key to successful automation is appointing an automation champion—a person or small team inside the company who leads the project.
- This champion understands both the shop floor and automation technologies.
- They coordinate with external automation integrators and vendors.
- Champions clarify goals, align teams, and oversee implementation timelines.
- They also monitor automation performance and guide training efforts.
Having a dedicated internal advocate is crucial since automation projects can become complex with risk of scope creep or unrealistic targets. Champions keep the process focused and documentation thorough.
Safety Considerations and Costs in Automation Projects
Automation brings safety benefits: less chemical exposure, reduced heavy lifting, and fewer manual interventions. But safety planning must be proactive:
- Risk Assessments: Identify hazards like pinch points, chemical leaks, or robot zones.
- Safety Interlocks: Install emergency stops, light curtains, and safety cages around robotic cells.
- Training: Ensure operators and maintenance staff follow strict protocols.
- Compliance: Adhere to standards such as OSHA or CE marking.
Include safety equipment costs in the initial automation budget. These expenses, though sometimes overlooked, are vital to protect workers and avoid costly accidents.
How Integrated Automation Improves Chemical and Process Control
In metal finishing steps like passivation and coating, automation tightly manages chemical dosing, heating, and rinse flow:
- Chemical Dosing: Automated pumps deliver precise amounts based on real-time sensor feedback to maintain concentration and limit waste.
- Heating Controls: Programmable controllers keep bath temperatures stable, improving coating adhesion.
- Rinse Flow: Sensors adjust water flow to minimize consumption while ensuring thorough rinse.
This tight control yields uniform treatment of all film batches, eliminates operator variability, and reduces chemical costs by up to 20%.
Training and Maintenance Practices for Automation Success
Automation systems are only as good as the people who operate and maintain them. Success depends on:
- Comprehensive Training: Teach operators the system interfaces, troubleshooting steps, and safety rules.
- Hands-on Practice: Simulated fault conditions prepare staff for real emergency handling.
- Preventive Maintenance: Schedule regular checks on equipment parts, sensors, and robots to avoid unexpected downtime.
- Documentation: Keep logs of maintenance activities and automation performance metrics to track improvements.
- Continuous Improvement: Use automation data to identify future upgrades or fine-tuning areas.
The right training and maintenance practices reduce breakdowns and maximize uptime, ensuring a strong return on automation investments.
Summary Table: Automation Elements in Metalized Film Manufacturing
| Automation Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Automation Types | Robots, cobots, simple automation devices |
| Key Technologies | Roll-to-roll handling, inline sensors, continuous coating |
| Process Preparation | Mapping, standardizing, simplifying, ranking tasks |
| Automation Champion Role | Project coordination, vendor liaison, training oversight |
| Safety Costs | Interlocks, emergency stops, operator training |
| Process Control Improvements | Automated chemical dosing, heating, and rinse flow |
| Training & Maintenance | User training, preventive checks, performance logs |
Automation in metalized film manufacturing is a layered approach. The success lies in combining the right machines, detailed process planning, strong leadership, safety focus, and team skill-building. When done well, it enhances efficiency, product quality, safety, and overall competitiveness.
What Are the Emerging Trends and Future Benefits of Automation in Metalized Film Manufacturing?
Automation is shaping the future of metalized film manufacturing in exciting ways. Let’s explore how new technologies like AI and machine learning join forces with automation to boost sustainability, quality, and profits. I will also explain how these innovations help manufacturers keep up with market needs and regulations.
AI and Machine Learning in Metalized Film Manufacturing Automation
In metalized film manufacturing, AI and machine learning are transforming automation from simple robotic tasks into smart, self-learning systems. AI analyzes data from machines and production lines to detect patterns and predict issues before they happen.
For example:
- Predictive maintenance: AI tracks the wear and tear of equipment and schedules maintenance before breakdowns. This avoids costly downtime.
- Process optimization: Machine learning algorithms adjust coating thickness or metal deposition in real-time for better film quality.
- Adaptive control systems: AI-driven robots can handle variations in raw materials to keep production moving smoothly.
By integrating AI, manufacturers reduce waste, improve throughput, and increase product consistency.
Automation’s Role in Sustainability through Waste Reduction and Material Optimization
Sustainability is a key goal in metalized film production, and automation plays a big part here. Automated systems minimize material waste by controlling processes precisely.
Here’s how:
- Optimized material usage: Automation controls metal vapor deposition exactly to need, reducing excess material use.
- Reduced scrap rates: Automated inspection catches defects early, preventing waste of unusable films.
- Energy savings: Automated heating and chemical dosing systems use only needed amounts, lowering energy and chemical consumption.
In the long run, this cuts down environmental impact and lowers operating costs. For example, manufacturers have reported 15-25% waste reduction after automating rolling and coating lines.
Automated Inspection Technologies Enhance Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is critical for metalized films, especially in food packaging where barrier properties matter. Traditional metal detectors don’t work on metalized film because the metal content interferes with detection. That’s where advanced automated X-ray inspection systems come in.
Benefits include:
- Material density imaging: X-ray systems create grayscale images enabling detection of packing defects like broken seals or missing components.
- Chemical composition analysis: MDX and DEXA technologies reveal subtle issues in film layers.
- Mass and fill verification: These systems can measure package mass and verify contents without disrupting the production line.
Automated X-ray inspection improves product safety and compliance by catching defects early and reducing recalls.
Financial and Operational ROI from Incremental Automation Upgrades
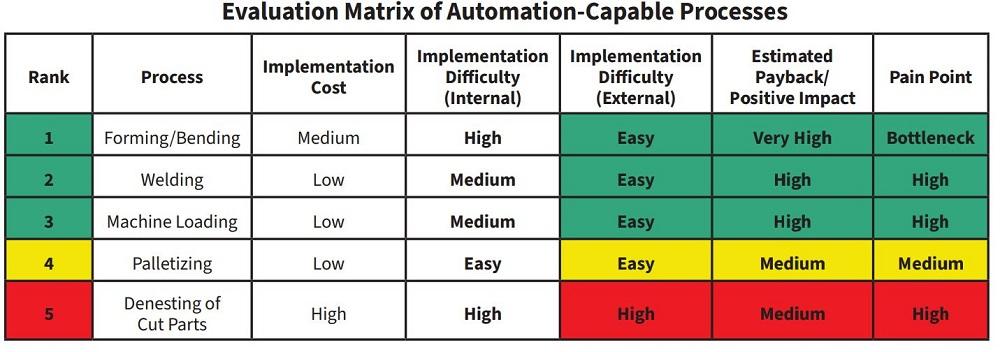
Manufacturers often hesitate to invest heavily in automation. But an incremental approach, focusing on high-impact bottlenecks, yields strong returns.
ROI highlights:
- Cost savings: Fewer labor hours and less scrap reduce expenses.
- Shorter lead times: Automation speeds up production cycles.
- Increased revenue: Higher production volume and consistent quality open new markets.
Table: Typical ROI Metrics from Automation Upgrades
| Automation Upgrade | Expected ROI Timeframe | Impact Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Roll-to-roll handling | 6-12 months | Throughput, waste reduction |
| Automated X-ray inspection | 12-18 months | Quality assurance, recalls |
| AI-driven process control | 18-24 months | Material optimization, uptime |
Incremental automation also spreads upfront costs, making projects more manageable.
Staying Competitive with Customization and Speed
Market demand is shifting toward smaller, customized product runs and faster turnaround. Automation helps meet these challenges by:
- Flexible cobots: Collaborative robots adapt to different product sizes quickly.
- Custom tooling: Automated tooling changes enable rapid design shifts without downtime.
- Continuous process flow: Roll-to-roll automation supports faster film production with minimal stops.
These advantages help manufacturers deliver what customers want, when they want it.
Automation and Compliance with Industry Standards
Regulations for metalized film packaging, especially in food, require strict quality and documentation controls. Automation supports compliance by:
- Consistent process control: Automated chemical baths maintain exact conditions meeting ASTM A967 standards and others.
- Electronic record-keeping: Automated logs track machine settings, maintenance, and inspection results, easing audits.
- Safety improvements: Reducing operator exposure to chemicals meets workplace safety laws.
Automation creates a robust framework to satisfy industry standards and avoid costly regulatory issues.
Table: Product Quality Improvements Due to Automation (Reinforced in Emerging Trends)
| Quality Metric | Before Automation | After Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Reduction (%) | — | 15-25% |
| Defect Rate | Higher | Lower |
| Energy & Chemical Savings (%) | — | Up to 20% |
The future of automation in metalized film manufacturing is bright. By blending AI, sustainable practices, and advanced inspection, manufacturers can boost quality, cut waste, and improve profits. These benefits come with faster, more flexible production that keeps pace with evolving markets and regulations. I encourage companies to approach automation as a strategic, phased journey. This way, they mitigate risks, build expertise, and gradually unlock success.
Additional Image to Showcase Automation Success Steps (Place at end as visual closing)
FAQs about Automation in Metalized Film Manufacturing:
What is automation in metalized film manufacturing?
Automation in metalized film manufacturing means using machines and technology to control production processes like metalizing, coating, cutting, and packaging with minimal human help, improving speed, accuracy, and safety.
How is automation implemented in metalized film manufacturing processes?
Automation in metalized film manufacturing processes is implemented by deploying industrial robots, collaborative robots (cobots), and simple automation devices combined with roll-to-roll handling technology, continuous processing, and rigorous process preparation including mapping and standardization.
What machinery and technologies are commonly used for automation in metalized film manufacturing?
Common machinery and technologies used include roll-to-roll handling systems, vacuum metallizing chambers, automated slitters and rewinders, industrial robots and cobots, sensors and machine vision systems, and advanced software platforms for process control and data collection.
How does automation improve product quality and consistency?
Automation improves product quality and consistency by maintaining precise metal coating thickness, using real-time monitoring with sensors to detect defects early, and documenting processes digitally, which significantly reduces variability and defect rates.
What are the key benefits of automation in metalized film manufacturing?
Key benefits of automation include reduced labor dependency, lower operating costs, higher throughput with less downtime, decreased material waste, improved workplace safety by minimizing manual handling, and enhanced sustainability through optimized material and energy use.
Automation in metalized film manufacturing uses advanced machines and systems to boost speed, cut costs, and improve quality. It solves key issues like labor shortages and supply-chain delays. Automation also raises safety standards and ensures consistent product output. Today, AI and smart tools push these gains further while supporting greener, more efficient production. If you want to stay competitive and meet rising demands, adopting automation is no longer a choice—it’s a must. I believe its impact will only grow stronger in this industry’s future.

